Install Mail Server - CentOS
OS: CentOS 6.5 - 64bits
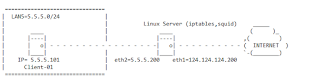
ServerName: mailsrv01.lnx.org
Server IP: 124.124.124.201
What we are going to set up:
1. Install and configure Postfix
2. Install and configure Dovecot
3. Install and configure Web Mail (Squirrel Mail)
1. Install and configure Postfix
yum install postfix
Copy the the original file
cp /etc/postfix/main.cf /etc/postfix/main.cf.orig
Edit main configuration file of postfix
vi /etc/postfix/main.cf
With content
myhostname = mailsrv01.lnx.org
mydomain = lnx.org
myorigin = $mydomain
inet_interfaces = all
inet_protocols = all
mydestination = $myhostname, localhost.$mydomain, localhost, $mydomain
mynetworks = 124.124.124.0/24, 127.0.0.0/8
home_mailbox = Maildir/
Restart postfix and enable in start up
service postfix restart
chkconfig postfix on
Create username : userlnx1 and set the password
useradd userlnx1
passwd userlnx1
Install telnet and test smtp
yum install telnet
telnet localhost smtp
ehlo localhost
mail from:
rcpt to:
data
welcome to LNX mail server
.
quit
ls /home/userlnx1/Maildir/new/
(We should see the file that contain the email content)
2. Install and configure Dovecot
yum install dovecot
Copy the original file
cp /etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf /etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf.orig
Edit File
vi /etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf
With content
protocols = imap pop3 lmtp
Copy the original file
cp /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf.orig
Edit File
vi /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf
With content
mail_location = maildir:~/Maildir
Copy the original file
cp /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-auth.conf /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-auth.conf.orig
Edit File:
vi /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-auth.conf
With content
disable_plaintext_auth = yes
auth_mechanisms = plain login
Copy the original file
cp /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-master.conf /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-master.conf.orig
Edit File
vi /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-master.conf
With content
## Line 83, 84 - Uncomment and add "postfix"
#mode = 0600
user = postfix
group = postfix
Start service and enable in start up
service dovecot start
chkconfig dovecot on
Test POP3
telnet localhost pop3
user userlnx1
pass rhce2015
retr 1
quit
3. Install and configure Web mail (Squirrel Mail)
Download and install CentOS 6. repostory
wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
rpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
Install Squirrelmail
yum install squirrelmail
Go to configure directory
cd /usr/share/squirrelmail/config/
and Run the perl script
./conf.pl
The following wizard will open. Enter choice “1” to set your organization details:
The following wizard will open. Enter “1” again to modify your organization details:
[SquirrelMail]:
LNX-Org
By this way, setup all the details such as organization title, logo, provider name in the above wizard.
Once you done, press “
S” to save changes and press “
R” to return back to your main menu:
Now enter “2” to setup mail Server settings such as domain name and mail agent etc.:
Enter “1”, Enter your mail domain (ex. lnx.org) and press Enter key.
Enter “3” and change from sendmail to Postfix MTA (i.e. SMTP):
Enter “2” to switch from sendmail MTA to postfix.
Now enter “
S” followed by “
Q” to save and exit Squirrelmail configuration.
Command >>
Q
Exiting conf.pl.
You might want to test your configuration by browsing to
http://your-squirrelmail-location/src/configtest.php
Happy SquirrelMailing!
Access to check the config of squirrelmail
http://124.124.124.201/webmail/src/configtest.php
If you got this error message
ERROR: Error connecting to SMTP server "localhost:25".Server error: (13) Permission denied
Run this command
setsebool httpd_can_network_connect=1
Allow port 25 in iptables
vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables
Add this line
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 25 -j ACCEPT
Restart iptables
/etc/init.d/iptables restart
Copy the original file
cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf.orig
Edit file
vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
With content
Alias /webmail /usr/share/squirrelmail
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
RewriteEngine On
AllowOverride All
DirectoryIndex index.php
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
Restart Apache
service httpd restart
Allow port 80 in iptables
Edit file
vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables
with this content
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
Restart iptables
/etc/init.d/iptables restart
Create username: userlnx2 and set the password
useradd userlnx2
passwd userlnx2
Log into webmail with user : userlnx1 and send email to userlnx2.
http://124.124.124.201/webmail/
and login as user: userlnx2 to check the mail mail server we can login and send the email.
Done,
#Postfix #Dovecot #Webmail #SquirrelMail #Vannak